Outline of Nonlinear Structural Analysis
On the ordered analysis work, generally the appropriate method is chosen and applied according to the analysis object and the contents of examination from the full three-dimensional solid analysis, the three-dimensional layered-shell analysis, the three-dimensional frame analysis based on fiber technique, whose code name above is COM3, and the two-dimensional plate analysis, whose code name above is WCOMD. These are across the board to the point that all methods are based on "the path-dependent material costitutive models of reinforced concrete panel (or uni-axis material constitutive models which dropped the dimension from them)" applicable for arbitrary loading paths.
Just these in-plane material constitutive models make the basis of the nonlinear structural response evaluation technology of concrete structures which result in from cracking, yielding and to ultimate state, and they have been developed over many years at the concrete laboratory, the University of Tokyo.
The strongest point of this analytical method is applicable to arbitrary structural shape and static/dynamic repeated loadings by aiming at formulation of the material constitutive models considering faithful path-dependency without prodiving qualification in coverage from the beginning. Moreover, in utilization of this technology, numerical stability and convergency are also encouraged, and gradually big results have gone up in this point in recent years.
Until now, it is proved through application, verification and competition participation of numerical simulation, etc. for various structures and members including Nuclear Energy Agency that it has high accuracy within and without our country.
#A part of example of analytical investigation is extracted and introduced at the page of "Application Example in Research".
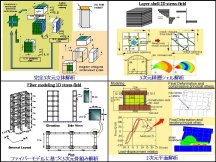 ü@ ü@

Pictures will be expanded when they are clicked.
Structural response is computed by superposition of mean stress computed from mean stress and mean strain relationships of concrete and reinforcing bar in the in-plane material constitutive models (see figures below). Here, the word "average" shows that the cracking and strain fields locally induced in RC is expressed on spatially average within the volume in which distributed cracks are introduced. (=Smeared Crack Approach )
In-plane constitutive models of concrete under teo-axes stress consist of elasto-plastic fracture model before cracking, compression and shear behavior along cracks, and tension behavior perpendicular to cracks. Although it becomes very important in RC constitutive models to take into consideration the interaction effect, bond of reinforcing bars and concrete, the concrete and steel behavior in RC include this, and are formulized in a different shape from the simplex behavior.
About the treatment of concrete cracks, it is one of the advantages of this analytical method that cracks in a maximum of four directions can be taken into considerationit faithfully based on loading history, and it contributes to the upswing in accuracy and enlargement of coverage. (=Multi-Directional Fixed Crack Approach )
Moreover, although a smeared crack approach is set on a standard, the analytical method is expanded in the applicable shape also to plain concrete by taking in knowledge of fracture mechanics, and the estimation accuracy of the large-sized structures which often possess roughness and fineness in steel arrangement is improved. Incidentally, this became a important point when taking size effect of shear failure into consideration.
Furthermore, in recent years, the upswing in analysis accuracy of highly inelastic range after the maximum capacity has been attained by establishing the constitutive models expressing buckling of reinforcing bars and time-dependency of concrete softening rule.
In addition, by modeling steel plate applied to planar members etc. and by formulizing respectively the joint elements for inserting between member connection joints or different materials, the upswing in practicality of the analytical method is aimed at. Please refer to references1),2) about the further details of the analytical method.
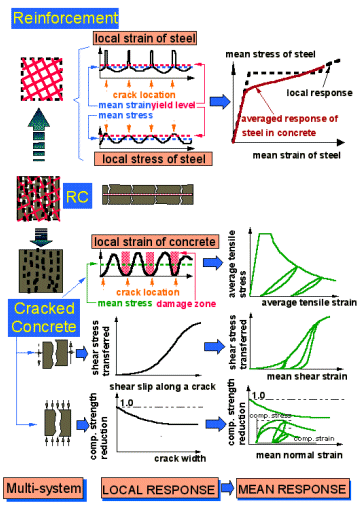 ü@ ü@
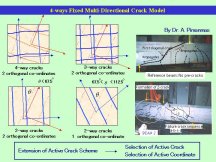
Pictures will be expanded when they are clicked.
References
| 1) |
Okamura, H. and Maekawa, K. : Nonlinear Analysis and Constitutive Models of Reinforced Concrete, Gihodo-Shuppan, 1991. |
|
| 2) |
Maekawa, K., Okamura, H. and Pimanmas, A. : Nonlinear Mechanics of Reinforced Concrete, SPON PRESS, 2003. |
|
|